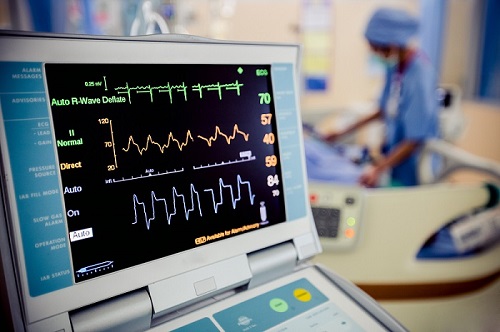
Have you ever wondered how doctors can see inside your heart without cutting you open? The answer lies in a remarkable device called an electrocardiogram (ECG) machine. This non-invasive tool allows medical professionals to monitor your heart’s electrical activity, providing crucial insights into its rhythm and function.
As you lie on an examination table, electrodes placed on your skin capture the faint electrical signals produced by your beating heart. But how exactly does an ECG machine transform these signals into the familiar peaks and valleys on a printout? In this article, you’ll discover the fascinating inner workings of ECG machines and their vital role in cardiac care.
What is an ECG Machine?
An ECG machine, or electrocardiogram machine, is a vital medical device used to monitor and record the electrical activity of the heart. This sophisticated piece of equipment plays a crucial role in diagnosing various heart conditions and assessing overall cardiac health.
The ECG machine works by detecting and amplifying the tiny electrical signals produced by the heart with each beat. Electrodes placed on specific areas of the patient’s body pick up these signals, which are then translated into a visual representation, typically a graph or waveform, that healthcare professionals can interpret.
ECG machines are indispensable tools in various medical settings, from emergency rooms to routine check-ups. They help doctors identify irregular heart rhythms, assess the effects of cardiac medications, and monitor patients with known heart conditions. The portability of modern ECG machines also allows for their use in ambulances and remote healthcare facilities, making this crucial diagnostic tool widely accessible.
What is an ECG machine Used For?
An ECG machine, or electrocardiogram machine, is a vital diagnostic tool in modern medicine. Its primary function is to monitor and record the electrical activity of the heart, providing healthcare professionals with crucial information about a patient’s cardiac health.
Diagnostic Applications
ECG machines are used to detect a wide range of heart conditions. They can identify irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias), assess the effects of certain medications on the heart, and monitor changes in heart activity over time. These devices are invaluable in diagnosing heart attacks, both ongoing and those that have occurred in the past.
Preventive Care
Beyond acute diagnoses, ECG machines play a significant role in preventive cardiology. Regular ECG screenings can help detect early signs of heart disease, allowing for timely intervention and potentially life-saving treatments. They’re often used in routine check-ups for patients with a history of heart problems or those at high risk for cardiovascular disease.
Monitoring During Procedures
ECG machines are also essential during various medical procedures. They provide real-time feedback on a patient’s heart activity during surgeries, stress tests, and other medical interventions. This continuous monitoring ensures patient safety and allows medical professionals to respond quickly to any cardiac events that may occur.
In summary, the ECG machine is a cornerstone of cardiac care, offering vital insights into heart health and function across a spectrum of medical scenarios.
The History and Evolution of the ECG Machine
The ECG machine has come a long way since its humble beginnings. Let’s take a journey through time to see how this vital medical device has transformed over the years.
Back in the late 19th century, scientists were just beginning to understand the electrical activity of the heart. In 1887, Augustus Waller recorded the first human electrocardiogram using a capillary electrometer. But it wasn’t until Willem Einthoven’s string galvanometer in 1901 that the modern ECG machine truly began to take shape.
Einthoven’s invention was a game-changer. It allowed for more accurate recordings of heart activity, earning him the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1924. However, these early machines were massive – some weighing up to 600 pounds!
As technology advanced, so did the ECG machine. The 1930s saw the introduction of vacuum tube amplifiers, making the devices more portable and easier to use. By the 1960s, transistors had replaced vacuum tubes, further reducing size and improving reliability.
The late 20th century brought about a seismic shift in ECG technology. Digital signal processing and microprocessors transformed these machines into the compact, user-friendly devices we know today. Modern ECG machines can now automatically interpret results, store data electronically, and even transmit information wirelessly to healthcare providers.
The evolution of the ECG machine continues. With the rise of wearable technology and artificial intelligence, we’re seeing new innovations like smartwatch ECGs and AI-assisted diagnosis. Who knows what the future holds for this indispensable medical tool?
How an Electrocardiogram (ECG) Machine Works
Ever wondered how that mysterious ECG machine at your doctor’s office actually works? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of electrocardiography and uncover the secrets behind this life-saving technology.
At its core, an ECG machine is designed to measure and record the electrical activity of your heart. Your ticker is like a tiny power plant, generating electrical impulses that make it beat. The ECG machine captures these signals and translates them into those squiggly lines you’ve probably seen on medical dramas.
Electrodes: Your Heart’s Storytellers
When you’re hooked up to an ECG machine, small sticky patches called electrodes are placed on specific areas of your body. These little guys are like reporters, picking up the electrical signals from different angles. Usually, there are 10 electrodes placed on your chest, arms, and legs.
From Heartbeat to Graph
Once the electrodes are in place, the ECG machine goes to work. It amplifies the tiny electrical signals and converts them into a visual representation. The result? Those familiar peaks and valleys on graph paper or a digital screen. Each part of this waveform tells a story about different phases of your heartbeat.
While the ECG machine does the heavy lifting of recording your heart’s electrical activity, it takes a trained eye to interpret the results. Doctors and specialists analyze the patterns to detect various heart conditions, from irregular rhythms to potential blockages.
Remember, an ECG machine is just one tool in a doctor’s arsenal. It’s incredibly useful, but it’s often used alongside other tests to get a complete picture of your heart health.
Key Components of an ECG Machine
An ECG machine is a complex device with several crucial components working together to capture and interpret the heart’s electrical activity. Let’s dive into the some of the key components that make this medical marvel tick:
Electrodes and Leads
The journey of an ECG starts with electrodes. These sticky sensors attach to your skin, picking up the heart’s electrical signals. Connected to the electrodes are leads, wires that transmit these signals to the ECG machine for processing.
Amplifier
Once the electrical signals reach the ECG machine, they’re pretty weak. That’s where the amplifier steps in, boosting these tiny signals to make them easier to analyze and record.
Filters
Not all electrical activity picked up by the electrodes comes from your heart. Filters help remove unwanted noise from other sources, like muscle movements or electrical interference, ensuring a cleaner, more accurate reading.
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
The ADC is the bridge between old-school and new-school tech. It takes the analog signals from your body and converts them into digital data that computers can understand and process.
Microprocessor
Think of this as the ECG machine’s brain. The microprocessor takes the digital data and applies complex algorithms to analyze the heart’s rhythm and electrical patterns.
Display Screen
This is where the magic becomes visible. The display screen shows the familiar ECG waveform, allowing healthcare professionals to visually interpret your heart’s activity.
Printer
For a hard copy of your heart’s performance, the printer component can produce a paper readout of the ECG tracing. This is often attached to your medical records.
Storage and Transmission System
Modern ECG machines can store your results digitally and even transmit them to other medical facilities or specialists for further analysis. This component is crucial for telemedicine and remote consultations.
Understanding these components gives you a glimpse into the intricate workings of an ECG machine, showcasing how this vital diagnostic tool captures the complex electrical symphony of your heart.
Understanding the ECG Waveform and Measurements
When you’re looking at an ECG machine readout, you might feel like you’re trying to decipher an alien language. But don’t worry! With a little know-how, you’ll be reading those squiggly lines like a pro in no time.
The PQRST Complex: Your Heart’s Signature
At the heart of every ECG waveform (pun intended) is the PQRST complex. This sequence of waves represents the electrical activity in your ticker during a single heartbeat. Let’s break it down:
- P wave: This little bump signals your atria contracting.
- QRS complex: The big spike in the middle? That’s your ventricles saying “Let’s do this!”
- T wave: The final wave shows your ventricles relaxing and recharging.
Measuring the Beats
The ECG machine doesn’t just draw pretty pictures – it’s all about the numbers. Here are some key measurements to keep an eye on:
- Heart rate: How many times your heart beats per minute.
- PR interval: The time it takes for an electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
- QT interval: This measures how long it takes your ventricles to contract and relax.
What Those Squiggles Really Mean
Now, you might be wondering, “Why should I care about all these waves and intervals?” Well, they can tell you a lot about your heart health. Abnormalities in the waveform can indicate various conditions, from harmless irregularities to serious heart problems.
Remember, while it’s fun to play amateur cardiologist, always leave the final interpretation to the pros. Your doctor knows best when it comes to decoding the messages your heart is sending through the ECG machine.
Preparing for an ECG Test
Getting ready for your ECG test doesn’t have to be stressful. With a few simple steps, you can ensure a smooth and accurate experience. Here’s what you need to know:
Before Your Appointment
First things first, chat with your doctor about any medications you’re taking. Some meds can affect your heart’s electrical activity, potentially impacting your ECG results. Don’t stop taking any prescribed medications without your doctor’s okay, though!
On the day of your test, skip the lotions and oils. These products can interfere with the electrodes’ ability to stick to your skin and pick up those all-important electrical signals. Also, leave your jewelry at home, metal can mess with the ECG machine’s readings.
What to Wear
Comfort is key when it comes to your ECG test outfit. Opt for loose-fitting, easy-to-remove clothing. A two-piece outfit works best, as you’ll need to bare your chest and ankles for the electrodes.
During the Test
When you arrive, you’ll be asked to lie down on an exam table. Try to relax, deep breaths can help calm any nerves. The technician will attach small, sticky electrodes to your chest, arms, and legs. These little sensors are the ECG machine’s way of “listening” to your heart’s electrical symphony.
Remember, an ECG is painless and typically takes just a few minutes. So lie back, take it easy, and let the ECG machine do its thing. Before you know it, you’ll be one step closer to understanding your heart health better.
Interpreting ECG Results: What Do They Mean?
When it comes to understanding your heart health, deciphering an ECG machine’s output can seem like cracking a secret code.
The Basics of ECG Waves
An ECG machine records the electrical activity of your heart, producing a series of waves. Each wave represents a different phase of your heartbeat:
- P wave: Atrial contraction
- QRS complex: Ventricular contraction
- T wave: Ventricular relaxation
What Doctors Look For
Your doctor isn’t just admiring the artistic qualities of your ECG. They’re searching for specific patterns that could indicate:
- Heart rate: Is it too fast, too slow, or just right?
- Heart rhythm: Are the beats regular or irregular?
- Conduction abnormalities: Is the electrical signal moving properly through the heart?
- Signs of heart attack or ischemia: Are there changes in the ST segment or T wave?
Red Flags and Warning Signs
While only a medical professional can provide a definitive interpretation, there are some patterns that might raise eyebrows:
- Unusually tall or wide QRS complexes
- Inverted T waves
- ST segment depression or elevation
- Missing P waves or extra waves
Remember, an abnormal ECG doesn’t always mean trouble. Sometimes it’s just your heart’s unique “signature.” That’s why it’s crucial to have a skilled interpreter who can put your ECG results in context with your overall health picture.
Common Uses and Applications of ECG Machines
The ECG machine is a versatile tool with numerous applications in healthcare. Here are seven common uses that highlight its importance:
Detecting Heart Rhythm Abnormalities
ECG machines excel at identifying irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias. By analyzing the electrical signals from your heart, these devices can spot patterns that may indicate conditions like atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
Diagnosing Heart Attacks
During a heart attack, the ECG machine becomes crucial. It can detect subtle changes in the heart’s electrical activity, helping doctors quickly identify and respond to cardiac emergencies.
Monitoring Heart Health in Chronic Conditions
For patients with ongoing heart issues, regular ECG tests are vital. The ECG machine provides valuable data on how well medications are working and whether adjustments are needed.
Pre-operative Assessments
Before surgery, an ECG machine helps evaluate a patient’s cardiac health. This information is critical for anesthesiologists and surgeons to plan safe procedures.
Fitness and Athletic Performance
Even outside clinical settings, ECG machines play a role. Athletes often undergo ECG tests to assess their heart’s performance and ensure they’re in top condition for competitions.
Stress Tests
When combined with exercise, the ECG machine becomes a powerful diagnostic tool. Stress tests can reveal heart problems that might not be apparent at rest.
Research and Clinical Trials
In the world of cardiology research, ECG machines are indispensable. They provide objective data for studies on new treatments and help advance our understanding of heart health.
Frequently Asked Questions
These are some frequently asked questions and answers about an ECG machine.
How often should I get an ECG?
The frequency of ECG tests depends on individual health factors. For healthy adults, an ECG might be part of a routine physical exam every few years. However, those with heart conditions or risk factors may need more frequent ECGs. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Are ECG machines safe?
ECG machines are generally very safe. The test is non-invasive and painless, simply involving the placement of electrodes on the skin. There’s no risk of electric shock as the machine only records electrical activity; it doesn’t send electricity into the body.
Can I perform an ECG at home?
While professional ECG machines are typically used in medical settings, there are now portable ECG devices available for home use. These can be helpful for monitoring certain conditions, but they shouldn’t replace regular check-ups with a healthcare provider. Always discuss the use of home ECG devices with your doctor.
Conclusion
As you’ve learned, ECG machines play a vital role in modern cardiology. By detecting and recording the heart’s electrical activity, these sophisticated devices provide invaluable data for diagnosing and monitoring cardiac conditions.
Understanding how ECG machines work empowers you as a patient or healthcare professional to better interpret results and appreciate their significance. While technology continues to advance, the fundamental principles behind electrocardiography remain essential to cardiovascular care. Whether you encounter an ECG as part of a routine checkup or in an emergency situation, you can now approach the procedure with greater knowledge and confidence.