A password alone isn’t enough to protect your online accounts. Two-factor authentication (2FA) has emerged as a critical security measure that adds an extra layer of protection to your digital life. Think of it as a double-lock system for your online accounts – even if someone cracks your password, they still can’t get in without the second key.
The rising tide of cyber threats has made 2FA more relevant than ever:
- Over 15 billion passwords were exposed in data breaches in 2020
- Credential stuffing attacks increased by 300% in 2021
- 80% of data breaches are linked to weak or stolen passwords
2FA works by requiring two different forms of verification:
- Something you know (your password)
- Something you have (like your phone for verification codes)
The digital landscape has become increasingly hostile, with cybercriminals using sophisticated methods to breach accounts. Your social media, banking, email, and other online services contain valuable personal information that needs robust protection. 2FA acts as your digital bodyguard, standing between your sensitive data and potential threats.

Understanding and implementing 2FA isn’t just a security choice – it’s becoming a necessity. As our lives become more intertwined with digital services, protecting your online presence with 2FA helps ensure your digital identity stays secure in an increasingly connected world.
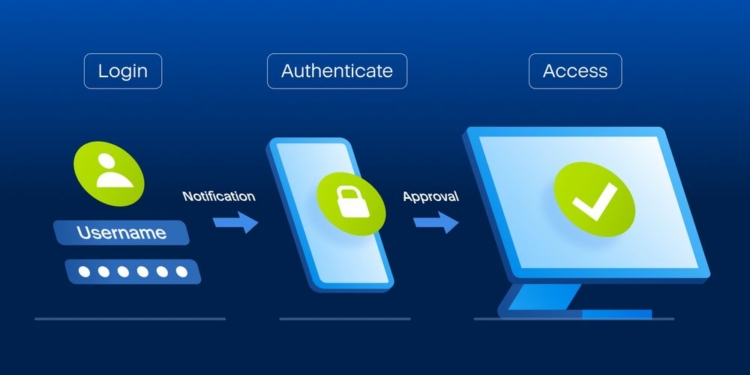
What is Two-Factor Authentication and How Does It Work?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a critical security layer to your online accounts by requiring two distinct forms of verification. Unlike traditional login methods that rely solely on a username and password combination, 2FA demands additional proof of identity – typically a temporary code – before granting access.
The Two-Step Verification Process:
- First Authentication Factor: Enter your username and password
- Second Authentication Factor: Input a unique verification code
This dual-layer approach creates a robust security barrier. Think of it as a double-lock system – you need both a key (password) and a temporary access card (verification code) to enter.
How 2FA Generates and Handles Codes:
- Each verification code is uniquely generated for a specific login attempt
- Codes typically expire within 30-60 seconds
- Once used, a code becomes invalid and cannot be reused
- New codes are automatically generated for each login session
The Security Logic Behind 2FA:
A hacker might crack your password through various methods:
- Brute force attacks
- Phishing attempts
- Data breaches
- Password database leaks
With 2FA enabled, stolen passwords become useless without access to your verification codes. The temporary nature of these codes adds another security dimension – even if intercepted, they quickly become invalid.
Authentication Methods:
Your second factor can be:
- A code sent via SMS
- A code generated by an authenticator app
- A physical security key
- Biometric data (fingerprint or face recognition)
This multi-layered approach transforms your account security from a single point of failure into a dynamic, two-step verification process. Each layer operates independently, creating a significantly more secure authentication system than traditional password-only methods.
Methods to Get Verification Codes for 2FA
You can receive your two-factor authentication codes through two primary methods: SMS text messages or authenticator apps. Each method has distinct advantages and security implications.
SMS Method
The SMS method sends verification codes directly to your phone number through text messages. Here’s what you need to know:
Advantages of SMS verification:
- Quick setup process
- No additional apps required
- Familiar method for most users
- Works on any mobile phone
Security concerns with SMS:
- Vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks
- Possible interception of text messages
- Dependent on cellular network coverage
- Risk of delayed message delivery
Authenticator App Method
Authentication apps like Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator generate verification codes directly on your device.
Benefits of authenticator apps:
- Works without internet connection
- Generates codes instantly
- Higher security than SMS
- No risk of message interception
- Multiple accounts in one place
Using authenticator apps:
- Download your preferred authenticator app
- Scan the QR code provided by your account
- Access codes directly from the app
- Codes refresh automatically every 30 seconds
The authenticator app method provides superior security compared to SMS verification. When hackers attempt account breaches, they can potentially intercept SMS messages through various techniques. Authentication apps eliminate this risk by generating codes locally on your device.
Many services support both methods, but security experts recommend using authenticator apps whenever possible. Apps like Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator can store multiple accounts, making it convenient to manage 2FA codes for different services in one secure location.
Setting Up Two-Factor Authentication with Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator App
Setting Up Google Authenticator
Setting up Google Authenticator requires a few simple steps:
- Download the Google Authenticator app from your device’s app store
- Open the app and tap the “+” icon
- Select “Scan QR code” or “Enter setup key”
- Navigate to your account’s security settings and locate the 2FA setup option
- Scan the displayed QR code with your phone’s camera
- Enter the verification code shown in the app to complete setup
Pro Tips for Google Authenticator:
- Take screenshots of backup codes provided during setup
- Write down recovery codes in a secure location
- Enable 2FA on one account at a time to avoid confusion
- Test the authentication process before logging out
Setting Up Microsoft Authenticator
Microsoft Authenticator setup follows a similar pattern:
- Install Microsoft Authenticator from your app store
- Launch the app and sign in with your Microsoft account
- Choose “Add account” from the menu
- Select account type (Microsoft, work/school, or other)
- Follow the on-screen prompts to scan QR code
- Verify setup by entering the displayed code
Microsoft Authenticator Features:
- Cloud backup of account credentials
- Push notifications for one-tap approval
- Password-free sign-in options
- Multi-account support with clear labels
Services Supported by Both Apps
Both apps support a wide range of services beyond their respective platforms. You can add accounts from popular services like:
- Social media platforms
- Email providers
- Banking applications
- Cloud storage services
- Password managers
Remember to keep your authenticator apps updated and maintain backup access methods for your accounts.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication brings substantial security benefits to your digital accounts, yet it also presents certain challenges worth considering.
Key Benefits:
- Prevents Account Takeovers: Even if hackers obtain your password through data breaches or phishing attacks, they can’t access your account without the second verification factor
- Protects Against Credential Stuffing: Cybercriminals can’t use stolen username/password combinations to break into your accounts
- Alerts You to Unauthorized Access: You’ll receive verification codes when someone attempts to log in, warning you of potential security breaches
- Safeguards Financial Transactions: Many banks require 2FA for large transfers, preventing unauthorized withdrawals
Real-World Protection Examples:
A 2022 study by Microsoft revealed that 2FA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks. When Target experienced a major data breach, accounts protected by 2FA remained secure despite exposed passwords.
Notable Drawbacks:
- Time Investment: The extra verification step adds 15-30 seconds to each login process
- Device Dependency: You must have access to your phone or authentication device to log in
- Connectivity Issues: Poor internet or cellular service can prevent receiving verification codes
- Travel Complications: International travel may affect SMS delivery or app accessibility
- Battery Concerns: A dead phone battery can lock you out of your accounts
Specific Travel Considerations:
- Download backup codes before international trips
- Set up alternative verification methods when available
- Consider offline authentication apps for areas with limited connectivity
- Keep authentication devices charged and accessible during travel
The security benefits of 2FA significantly outweigh these inconveniences, making it a crucial tool in your digital security arsenal. Understanding both advantages and limitations helps you implement 2FA effectively across your accounts while preparing for potential challenges.
Implementing Two-Factor Authentication Across Your Online Accounts
Your digital life spans multiple platforms, each holding valuable personal information. Here’s a comprehensive list of accounts that need 2FA protection:
High-Priority Accounts:
- Banking and financial institutions
- Investment platforms
- Credit card accounts
- Tax filing services
- Government portals
- Healthcare providers
Personal Data Accounts:
- Email services
- Cloud storage platforms
- Password managers
- Digital payment services (PayPal, Venmo)
- Shopping accounts with stored payment info
- Social media profiles
Professional Accounts:
- Work email and communication tools
- Remote access systems
- Project management platforms
- Client management systems
- Business banking accounts
Each platform stores different pieces of your digital identity. Your social media accounts contain personal photos and conversations. Shopping platforms hold your credit card information and shipping address. Work accounts give access to sensitive company data.
A strategic approach to implementing 2FA starts with your most critical accounts. Begin with financial institutions and email accounts – these serve as gateways to your other services through password reset functions. Move systematically through your list, enabling 2FA on each platform that offers this security feature.
Remember: A single compromised account can create a domino effect, potentially exposing your other accounts to unauthorized access. Protecting each account with 2FA creates multiple barriers against potential security breaches.
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication is a crucial defense mechanism in our digital world. With the increase in cyber threats, it’s important to secure your accounts beyond just using passwords. By implementing 2FA, you create a strong security barrier that greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to your sensitive information.
Take action today:
- Enable 2FA on your banking and financial accounts
- Secure your social media presence with verification codes
- Protect your email accounts using authenticator apps
- Set up 2FA for your cloud storage services
Your online security matters. Every account you protect with 2FA strengthens your digital fortress. The time spent setting up and using 2FA is nothing compared to the potential consequences of a hacked account. Make the smart choice – make two-factor authentication your standard security practice.
Discussion about this post