Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes several chronic conditions that cause inflammation in the gut. Two main types are chronic inflammatory conditions that lead to a lot of discomfort and health problems.
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are different in where they affect the body and their symptoms. Knowing the differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. Both conditions can get worse and better over time, making it hard to manage.
It’s important for doctors to know the difference between these two chronic inflammatory conditions to create effective treatment plans. This article will compare Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. We’ll look at their symptoms, complications, and treatment options.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of conditions that cause long-term inflammation in the GI tract. It includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions lead to symptoms that can really impact your life.
The GI tract is key for digestion, absorbing nutrients, and getting rid of waste. IBD messes with these functions, causing symptoms like diarrhea, pain, tiredness, and weight loss. Knowing about IBD helps manage its symptoms and improve your gut health.
GI disorders like IBD can seriously affect your digestive system. The ongoing inflammation from IBD can cause serious problems if not treated. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment is key to controlling symptoms and avoiding damage to your GI tract.
| Condition | Affected Area | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Crohn’s Disease | Any part of the GI tract | Diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss |
| Ulcerative Colitis | Colon and rectum | Diarrhea, blood in stool, abdominal pain |
Understanding IBD is the first step to better management. By knowing the differences between Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, doctors can create better treatment plans. This helps improve the lives of those with these conditions.
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Crohn’s disease is a type of IBD that causes chronic inflammation. This inflammation can lead to serious complications. It can affect any part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the anus.
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. Patients may also experience weight loss and malnutrition. These symptoms can change in severity and may come and go.
Understanding Crohn’s disease is key to finding the right treatment. If not managed, it can cause the intestine to narrow, create fistulas, and abscesses. Treatment often includes medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
Crohn’s disease is different from other IBDs like ulcerative colitis. It can affect any part of the digestive system. This makes it important for doctors to choose the right treatment.
Knowing about Crohn’s disease helps patients manage their condition better. This knowledge lets them take an active role in their treatment. It improves their quality of life.
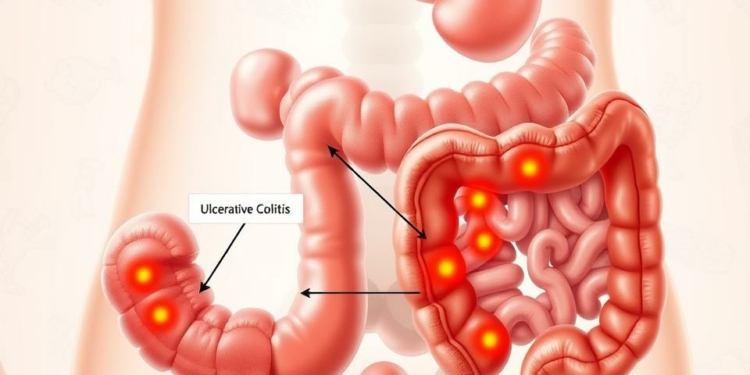
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the colon’s lining. It only affects the colon and rectum, leading to ongoing inflammation and ulcers. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, urgency, and abdominal pain, which can greatly affect a person’s life.
The inflammation in ulcerative colitis can cause ulcers and bleeding. It’s different from Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the digestive system. Knowing this is key to finding the right treatment options and managing the condition well.
It’s important to understand how severe ulcerative colitis is to plan treatment. Some people have mild symptoms, while others face more serious issues. Keeping the digestive system healthy is critical for managing ulcerative colitis and avoiding complications.
Treatment for ulcerative colitis often includes medicines to reduce inflammation and control symptoms. Sometimes, surgery is needed to remove the affected colon part. By understanding ulcerative colitis and its effects, doctors can tailor treatments to help patients better.
Crohn’s Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis: Key Differences
Managing Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis starts with knowing their differences. These are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) but affect the gut in different ways.
Crohn’s disease can hit any part of the digestive tract, from mouth to anus. It often targets the ileum, the lower small intestine. Ulcerative colitis, by contrast, only affects the colon. It causes ulcers and inflammation in the inner lining.
The inflammation’s depth also differs. Crohn’s disease can cause deep inflammation, affecting all bowel layers. This might lead to strictures and fistulas. Ulcerative colitis, though, has superficial inflammation, mainly in the colon’s mucosa and submucosa.
| Characteristics | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis |
|---|---|---|
| Location of Inflammation | Any part of the digestive tract | Limited to the colon |
| Depth of Inflammation | Deep, through all layers of the bowel wall | Superficial, limited to mucosa and submucosa |
| Common Complications | Strictures, fistulas, abscesses | Toxic megacolon, colon cancer |
It’s vital to understand these key differences for effective diagnosis and treatment. By knowing the unique traits of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, doctors can create personalized treatment plans for each patient.
Symptom Comparison: Digestive Manifestations
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis share some common symptoms. But, they also have key differences. Both are marked by chronic inflammation in the GI tract, leading to various symptoms.
Both conditions can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. But, the severity and nature of these symptoms differ. Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the GI tract. Ulcerative colitis mainly affects the colon.
- Diarrhea, which can be bloody in both conditions
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Weight loss due to malabsorption and loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting, more commonly associated with Crohn’s disease
A key difference is in the location and extent of inflammation. Crohn’s disease can cause patchy inflammation anywhere in the GI tract. Ulcerative colitis causes continuous inflammation in the colon. This affects symptoms and severity.
In terms of specific symptoms, Crohn’s disease is more likely to cause:
- Fistulas and abscesses due to deep inflammation
- Narrowing of the intestine (stricture)
- Malabsorption of nutrients
On the other hand, ulcerative colitis is characterized by:
- Continuous inflammation of the colon’s mucosa
- Urgent need to defecate
- Bloody stools
Understanding these differences is key to managing these conditions well. It helps improve the quality of life for patients.
Symptom Comparison: Systemic Manifestations
People with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) often face symptoms beyond just digestive issues. Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can cause a wide range of symptoms. These symptoms can greatly affect a person’s health and quality of life.
Systemic symptoms include fatigue, fever, and weight loss. These happen because the inflammation spreads beyond the gut. It can affect the body more broadly.
Crohn’s disease can lead to serious complications like fistulas and abscesses. These can greatly impact a person’s health and well-being.
The table below shows the main systemic symptoms for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis:
| Systemic Manifestation | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Common | Common |
| Fever | Common | Less Common |
| Weight Loss | Common | Less Common |
| Fistulas and Abscesses | More Common | Rare |
It’s important to understand these systemic symptoms for managing IBD. This highlights the need for care that goes beyond just gut symptoms. It must address the body’s overall health.
Complications Specific to Each Condition
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are both forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). They have different complications that can affect patients a lot. Knowing these complications is key to finding good treatments.
Fistulas and Abscesses
Crohn’s disease often causes fistulas and abscesses. Fistulas are abnormal connections in the intestine or with other organs. Abscesses are pockets of pus in the intestine or tissues. These can cause serious infections and need surgery.
Another issue with Crohn’s is strictures. These are narrowings of the intestine from inflammation and scarring. Strictures can block the intestine, causing pain, vomiting, and constipation.
Toxic Megacolon
Ulcerative colitis can lead to toxic megacolon. This is when the colon gets very inflamed and dilated. It can’t move stool anymore. This is a serious condition that needs quick medical help to avoid a fatal rupture.
Colorectal Cancer Risk
Both Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis raise the risk of colorectal cancer. This is more likely in patients with long-term disease and a lot of colonic involvement. Regular colonoscopies are advised for early detection and prevention.
Managing IBD well means controlling symptoms and preventing complications. By knowing the specific risks of Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis, doctors can offer better treatments. This helps improve patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Approaches and Differentiation
To treat Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis well, we must first figure out which one it is. Doctors use a mix of clinical checks, endoscopy, and imaging to make this diagnosis.
First, doctors look at your medical history and do a physical check. They look for signs like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. These are common in both diseases.
Endoscopy is key in diagnosing IBD. It lets doctors see inside your gut and take tissue samples. This helps tell if you have Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis. For instance, ulcerative colitis starts in the rectum and goes up, while Crohn’s can be anywhere.
Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, and MRI help see how far the disease has spread. They also spot problems like strictures, fistulas, and abscesses that Crohn’s can cause.
Here’s a quick rundown of how doctors diagnose:
- They check your symptoms and medical history.
- Endoscopy lets them see inside and take samples.
- Imaging tests show how far the disease has spread and if there are complications.
By using these methods together, doctors can tell if you have Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis. This helps them give you the right treatment.
Treatment Strategies for Both Conditions
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis aim to reduce inflammation and induce remission. Treatment options include medications and lifestyle changes.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs are key in treating both conditions. They help manage symptoms by reducing inflammation. Aminosalicylates are often used and can be taken orally or rectally.
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressants help control the immune system, reducing inflammation. They are used when other treatments fail. Common ones include azathioprine and mercaptopurine.
Biologics
Biologic therapies target inflammation-causing proteins. Infliximab and adalimumab are effective in managing symptoms. They help induce remission in both diseases.
The right treatment depends on the condition’s severity and the patient’s past responses. A healthcare provider will create a personalized plan.
Quality of Life and Long-term Outlook
People with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis face big challenges. These conditions affect their quality of life a lot. They can cause a lot of digestive and body problems.
Managing these conditions well is key to a better life. With the right treatment, people with IBD can live active and happy lives. They need ongoing care to control symptoms, avoid complications, and stay healthy.
Healthcare providers can make a big difference by understanding the differences between Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis. They can create treatment plans that meet each patient’s needs. This approach can greatly improve life quality and outlook for those with IBD.
Discussion about this post