How much do you know about Nigeria’s geopolitical zones? If the answer is “not much,” then you’re in the right place! In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into Nigeria’s geopolitical zones and break them down for you.
We’ll cover how many geopolitical zones there are in Nigeria, which states they include, typical activities that take place in each zone, and much more. Plus, to make it even easier to wrap your head around these concepts, we’ll include a map so you can visualize exactly where these Nigerian zones are located.
Let’s start by getting an understanding of what a geopolitical zone is, not just in Nigeria but in general. Once that’s established, we’ll move on to a rundown of each Nigerian zone’s characteristics and the states they incorporate.
What Are Geopolitical Zones in Nigeria
Geopolitical zones are basically divisions of the country, created to bring people together and provide ease of governing. These zones are composed of states that share certain cultural, historical, and environmental characteristics.
Let’s take a quick look at the geopolitical zones in Nigeria.
How many Geopolitical Zones are in Nigeria?
Nigeria is divided into six geopolitical zones, each of which has multiple states. These are the North Central, North East, North West, South East, South-South, and South West geopolitical zones.
Below is a breakdown of each zone and the states that make up each zone:
North Central
- Plateau State
- Niger State
- Kwara State
- Nasarawa State
- Abuja (Federal Capital Territory)
- Koji Stare
- Benue State
North East
- Taraba State
- Bauchi State
- Gombe State
- Adamawa State
- Borno State
- Yobe Stare
North West
- Kaduna state
- Zamfara State
- Katsina State
- Kano State
- Sokoto State
- Jigawa State
- Kebbi State
South East
- Abia State
- Imo State
- Anambra State
- Ebonyi State
- Enugu State
South South
- Edo State
- Akwa Ibom State
- Rivers State
- Bayelsa State
- Cross River State
- Delta State
South West
- Oyo State
- Osun State
- Ogun State
- Lagos State
- Ekiti State
- Ondo State
North Central (Middle Belt)
You may not have known that the North Central, also known as the Middle Belt part of Nigeria, consists of seven states, Plateau Niger, Nasarawa, Kwara, Kogi, Abuja, and Benue. Let’s take a look at each one of them.
The largest state in terms of area in the North Central region, Niger State has a diverse topography spanning the Niger River Valley to rolling hills dotted with cities like Minna, Suleja, and Bida.
Nasarawa State is home to a rich history dating back to pre-colonial times; Nasarawa State is mostly rural agricultural land, with a few small-scale industries like mining, textile manufacturing, and quarrying. The state also has several tourist attractions like caves and waterfalls, which draw visitors from all over Nigeria and beyond.
Kwara State was created during the military rule in Nigeria. It has since become an important industrial center with factories producing everything from automobiles to pharmaceuticals to textiles. The state is also rich in natural resources such as gold, iron ore, tin ore, lead ore, and coal reserves.
Kogi State is located in the heart of Nigeria and borders seven other states. It is also home to several natural resources such as coal, limestone, and tar sand deposits, as well as some small-scale industries such as agro-processing, smelting, and food processing.
Nigeria’s capital, Abuja, is ranked seventh in terms of population. The Federal Capital Territory (FCT) lies in the central part of Nigeria. The municipal hall, national cultural institutes, and other administrative buildings are located in the Central Area of the city of Abuja.
Abuja also houses the Three Arms Zone, which is where the presidential palace, the National Assembly, the Supreme Court, the National Arboretum, the National Christian Center, the National Mosque, and Millennium Park are located.
Benue is known for its unique topography; the state is primarily made up of hills and valleys and is considered to be the food basket of Nigeria due to its abundant agricultural production. It’s also one of the most populous states in the country.
The Middle Belt Zone, in terms of population, consists of about 20 million people, which accounts for 11% of the nation’s total population. The biggest city in this region is Abuja, the nation’s capital.
North East
The North East region is also known as “North East Nigeria,” and it includes six states: Taraba, Adamawa, Borno, Gombe, Yobe, and Bauchi.
The North East region has both a vast Sahara Desert area and some pretty lush tropical vegetation, including tree-filled savannahs. The wildlife in this area includes the endangered African Wild Dog, several antelope species, such as roan antelope and hartebeest, and many others. It also hosts a number of birds of prey and migratory ones too.
In terms of population, the North-East area of Nigeria is home to roughly 26 million people or about 12% of the country’s total population. Bauchi and Maiduguri are the two most populous cities in the region.
In terms of industry and commerce, North East Nigeria has an agricultural base that is quite diverse. Crops such as cotton and peanuts are grown here, too, because of the soil quality and climate. The region also has an active mining sector that mines gold, iron ore, columbite-tantalite (a mineral), lead-zinc ore, limestone, and coal, among other resources.
Overall, North East Nigeria is an interesting geopolitical zone that has much to offer in terms of beauty as well business opportunities.
North West
The North West zone is made up of seven states, which are: Kaduna, Kano, Katsina, Jigawa, Zamfara, Sokoto, and Kebbi.
The North West is home to some of the most densely populated cities in Nigeria, like Kano and Kaduna. North West geopolitical zone has a population of over 49 million people.
The major economic activities in the North West are large-scale farming and livestock rearing, along with small-scale trading. Farming and livestock rearing help provide food for not only the region but also other parts of Nigeria as well as export markets abroad. In addition to this, trading provides another way for people to make a living in the region.
Overall, this geopolitical zone is an important part of Nigeria due to its contributions in terms of economic activity.
South East
The South East zone consists of five states, including Abia, Anambra, Ebonyi, Enugu, and Imo. In terms of population size, this region is one of the most populous six geopolitical zones, with over 22,000,000 people living in the area, which is about 20% of the entire Nigeria population.
The South East zone is made up mostly of Igbo-speaking people and is known for its culture and traditional music. Other attractions include the National Museum in Enugu and the Imo Safari Park. Notable cities include Aba, Awka, and Owerri. Additionally, this region is known for its traditional festivals like New Yam Festival and Igbo Ukwu Festival.
Overall, the South East geopolitical zone offers a unique experience and culture that you can’t find anywhere else in Nigeria and maybe even the world!
South South
South-South is one of the geopolitical zones in Nigeria. This zone is made up of six states Akwa Ibom, Bayelsa, Cross River, Delta, Edo, and Rivers.
The region has vast oil reserves, but electricity and other infrastructure are limited. The South-South Zone’s economy is largely dependent on oil production and related industries, but it also has a smaller agricultural sector that’s growing fast. This zone accounts for about 40% of Nigeria’s proven oil reserves.
The South-South Zone is geographically subdivided into two parts: the Niger Delta region to the east and the coastal region to the west. It also contains some of Nigeria’s major rivers and wetlands, including Rivers Niger and Benue, that provide important sources of food, water, transport, and fuel for local communities.
South West
Let’s take a look at the South West. This zone comprises 6 states: Lagos, Ogun, Ondo, Ekiti, Osun, and Oyo.
Lagos is easily the most populous state in Nigeria and is known for its vibrant energy and economic opportunities. Ogun state with its many industrial factories and production plants. On the other hand, Ekiti, to the east of Ogun, is known for its rich agricultural lands that produce a variety of crops, including corn and cassava.
Ondo to the East boasts of several tourist attractions, including Igbokoda Beach and Idanre Hill, which attracts visitors from all over the country year-round. The capital of Osun to the North is a historic city filled with centuries-old relics like ancient churches and temples such as those found in Osogbo Sacred Grove. Lastly, Oyo, located in the Northwest, hosts many popular festivals, such as Egungun festivals, celebrated by Yoruba communities throughout Nigeria each year.
With its bustling cities, ancient relics, and rich culture, it’s easy to see why the South West geopolitical zone is one of Nigeria’s most populated regions!
Map of Geopolitical Zones in Nigeria
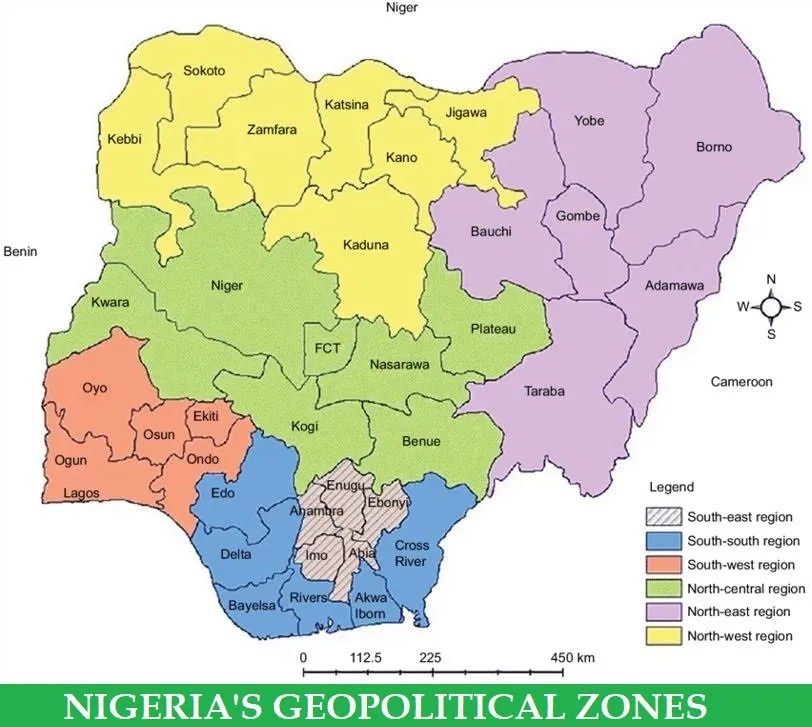
Each geopolitical zone has its own unique characteristics and consists of several states. By looking at a map of Nigeria’s geopolitical zones, you can quickly get an understanding of the country’s diversity.
Each of these zones has a unique history and culture that has contributed to making Nigeria one big family.
Advantages of Geo-Political Zones System in Nigeria
Nigeria is divided into six geopolitical zones. Let’s take a closer look at five potential advantages of having geopolitical zones in Nigeria.
Increase in unity
One of the advantages of having geopolitical zones in Nigeria is that it increases unity among the states and areas in each zone. This gives people living in each zone a sense of connection with the people living in other states in their zone.
Increased communication
Political zones can increase communication between different states since leaders from each state are able to communicate more easily with leaders from other states within their zone. This can help to foster a better relationship between different Nigerian states and improve communication between them.
Increased economic development
Another advantage of political zones is that they can promote economic development within the zone by encouraging trade between different states, as well as by promoting investment from outside sources into the zone. This can help to boost the economy of all the states within a particular zone.
Easier administration
Political zones make it easier for the Nigerian government to administer its policies since it can focus on specific needs for each particular zone instead of trying to manage everything across all states at once.
Improved representation
Having political zones makes it easier for elected representatives to represent their constituents as they are able to better understand and respond to their needs due to familiarity with their region or state’s needs and issues better than one who is not aware.
Conclusion
It’s fascinating to learn how Nigeria is divided into its different geopolitical zones. Not only can this help us better understand Nigeria’s political and economic climate, but it can also give us a better understanding of the cultural and linguistic differences between each zone.
Each geopolitical zone has its individual identity and its own sets of states, making it easy to identify and divide up the country’s regions for more in-depth analysis. Understanding the geopolitical zones of Nigeria can help us gain insight into the importance of regional identities in the country and allow us to better appreciate the diversity of the nation.








Discussion about this post